When you send and receive data over the wire, there are possibilities where the data can get corrupted, altered, or modified(it can be accidental, purposely done with evil intention). Whatever may be the case, there needs to be a method where the receiver can verify and figure out easily if the data is altered or corrupted.
Generally what happens is this..The sender calculates a short checksum value(very small in size) which represents the message/data that is being sent. The value calculated is either sent along with the message, or through other methods. Once the data is received, the receiver also calculates the checksum. If both the values(of the sender and the receiver) tallies, then the data is uncorrupted/unaltered.
 Sarath Pillai
Sarath Pillai Satish Tiwary
Satish Tiwary





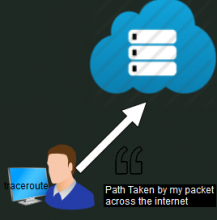
How Does Traceroute Work and Example's of using traceroute command
SAN vs NAS - Difference between a Storage Area Network and Network Attached Storage
difference between iterative and recursive dns query
Linux Booting Process: A step by step tutorial for understanding Linux boot sequence