static routing configuration


Before we go through the static routing configuration lets have a look why static routing is important and what is it's use.As you know static routing is most secure routing configuration.With the help of static routing a network administrator can configure each router with all appropriate routes.Static routing provides much control over how packets are passed through a network. And most important thing about static routing is that as we know routers are configured manually, so there are no routing protocols for hacker to manipulate.The only drawback of static routing is that it is not good for frequent route change.
Now let's concentrate on main motive of this article:
WHOM THIS POST IS FOR?
- One Who is preparing for ccna
- Network geeks.
- Intrested students in networking field.
- Network Administrators.
- Working Employees in Networking Field.
- Trainers and Facaulties related to Networking Field.
- Home use or for your own bussiness purpose.
- If you are running your own cyber cafe.
- If you are running LAN GAMING Bussiness.
WHAT DOES THIS "static routing" POST COVER?
How to configure port of a router.
How to perform static routing .
How to assign ip address on a ethernet port.
How to assign ip address on a serial port.
How to route path.
How to assign ip address on end devices.
how to change the Administrative Distance o fa static route.
How to ensure that static route remain permanent in routing table.
Learn about Floating Static Routes.
Learn about Default Routes and it's configuration.
how to remove static routes.
How to configure default routes.
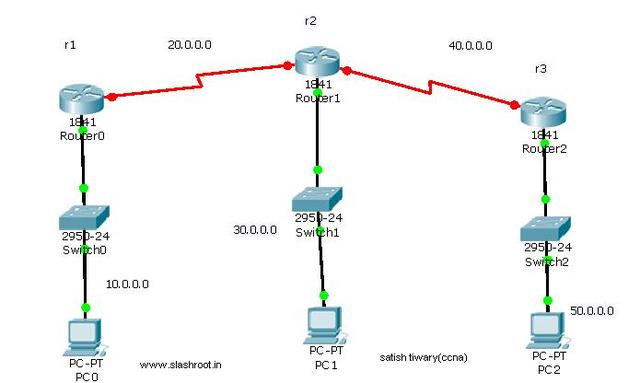
Explanation of Static Routing Configuration Using Diagram:
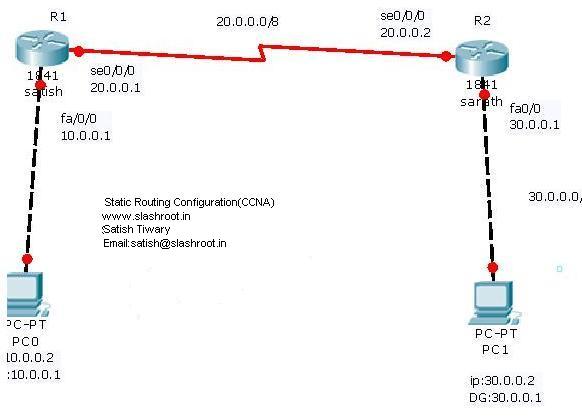
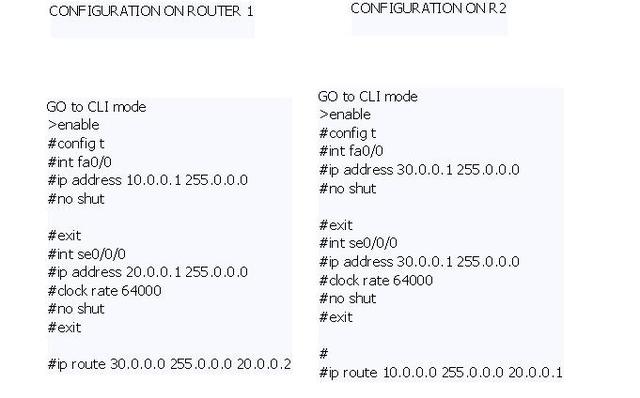
In above example
- 30.0.0.0 is the destination network255.0.0.0 is the subnet mask20.0.0.2 is the next hop IP
- ip address 20.0.0.1 255.0.0.0 is used to assign ip address and subnett mask on router interface.
- command int se0/0/0 order router configuration mode to shift on Serial Port 0/0/0.
- command int fa0/0 means Fast Etherenet port 0/0.
- no shut command is used to up the network or can say to up the interface,because the network by default the port is down.
- command clock rate 64000 is used to set clock rate on DCE device.
- ip route 30.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 20.0.0.2 tells the router about the other network present and which is directly not connected with that router.
How to configure Default Route?
To configure Default Route go to global configuration mode and type the following ios command.
• Router(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 default_gateway [administrative_distance]
OR
• Router(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 interface_to_exit [administrative_distance]
If you want to make this Default Route configuration Permanent then use the keyword permanent at last.
• Router(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 default_gateway [administrative_distance] [permanent]
OR
• Router(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 interface_to_exit [administrative_distance] [permanent]
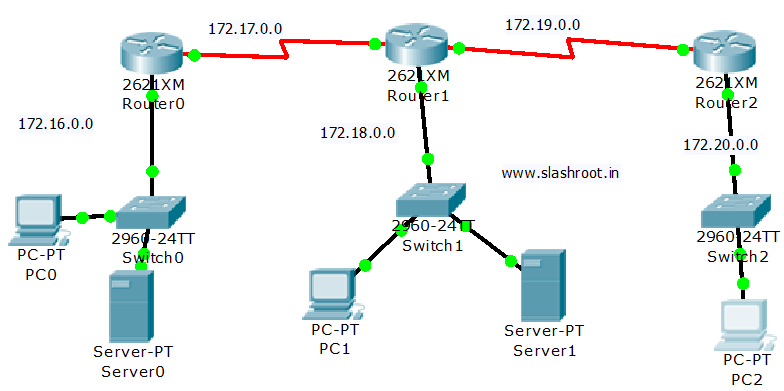
Router>enable Router#configure terminal #moves to global config mode Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Router(config)#hostname Router01 #configuring a router name Router01(config)#
Router01>enable #enable command is used to shift from user mode to previleged mode Router01#configure terminal #this command is used to shift from Privileged mode to Global configuration mode. Router01(config)#interface fa0/0 #interface mode i.e moves to interface fa0/0 Router01(config-if)#ip address 172.16.0.1 255.255.0.0 #Assign address and subnet mask to interface Router01(config-if)#no shutdown #Turns Interface on
Now Static Routing Configuration on ROUTER01:
Router01>enable Router01#configure terminal Router01(config)#interface s0/0 Router01(config-if)#clock rate 64000 Router01(config-if)#ip address 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Router01(config-if)#no shutdown
Router>enable Router#configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Router(config)#hostname Router02 Router02(config)#
Router02>enable Router02#configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Router02(config)#interface fa0/0 Router02(config-if)#ip address 172.18.0.1 255.255.0.0 Router02(config-if)#no shutdown
Router02>enable Router02#configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Router02(config)#interface s0/0 Router02(config-if)#ip address 172.17.0.2 255.255.0.0 Router02(config-if)#no shutdown
Router02>enable Router02#configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Router02(config)#interface s0/1 Router02(config-if)#clock rate 64000 Router02(config-if)#ip address 172.19.0.1 255.255.0.0 Router02(config-if)#no shutdown
Router>enable Router#configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Router(config)#hostname Router03 Router03(config)#
Router03>enable Router03#configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Router03(config)#interface fa0/0 Router03(config-if)#ip address 172.20.0.1 255.255.0.0 Router03(config-if)#no shutdown
Router03>enable Router03#configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Router03(config)#interface s0/1 Router03(config-if)#ip address 172.19.0.2 255.255.0.0 Router03(config-if)#no shutdown
config terminal
ip route network subnet nexthop
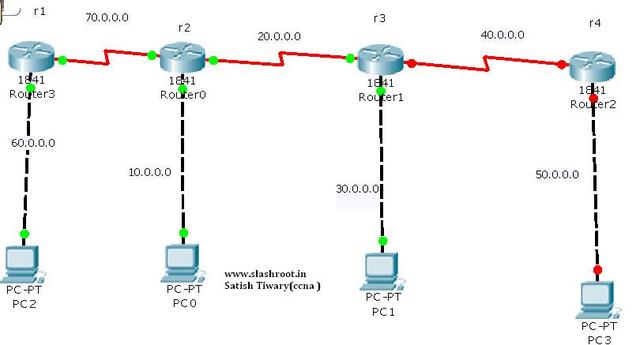
r1
config terminal
ip route 172.18.0.0 255.255.0.0 172.17.0.2
ip route 172.19.0.0 255.255.0.0 172.17.0.2
ip route 172.20.0.0 255.255.0.0 172.17.0.2
r2
config terminal
ip route 172.16.0.0 255.255.0.0 172.17.0.1
ip route 172.20.0.0 255.255.0.0 172.19.0.2
config terminal
ip route 172.18.0.0 255.255.0.0 172.19.0.1
ip route 172.15.0.0 255.255.0.0 172.19.0.1
ip route 172.16.0.0 255.255.0.0 172.19.0.1
no ip route 172.18.0.0 255.255.0.0 172.19.0.1

 Sarath Pillai
Sarath Pillai Satish Tiwary
Satish Tiwary
Add new comment